Biochemistry, Department of
Vadim Gladyshev Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
June 2006
Abstract
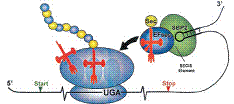
In the past several years, progress in genome sequencing and development of specialized bioinformatics tools allowed efficient identification of selenocysteine-containing proteins encoded in completely sequenced genomes. Information is currently available on selenoproteomes from a variety of organisms, including humans, which contain 25 known selenoprotein genes. This review provides basic information about mammalian selenoproteins and other known selenoprotein families. Analysis of full sets of selenoproteins in organisms provides exciting avenues for examining selenoprotein evolution and dependence of organisms on the trace element selenium and allows linking selenoproteins with specific biological and biomedical effects of dietary selenium.


Comments
Published in Selenium: Its molecular biology and role in human health, Second Edition, edited by Dolph L. Hatfield, Marla J. Berry, and Vadim N. Gladyshev. Springer Science+Business Media LLC, 2006. Pages 99–114. Copyright © 2006 Springer Science+Business Media LLC. Used by permission.