Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Kirill Belashchenko Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2012
Citation
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 85, 224414 (2012); DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.224414
Abstract
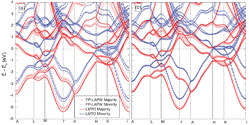
Spin-filter tunneling is a promising way to create highly-spin-polarized currents. So far the understanding of the spin-filtering effect has been limited to a free-electron description based on the spin-dependent tunneling barrier height. In this work we explore the complex of EuO as a representative ferromagnetic insulator used in spin-filter tunneling experiments and show that the mechanism of spin filtering is more intricate than it has been previously thought. We demonstrate the importance of the multiorbital band structure with an indirect band gap for spin-filter tunneling. By analyzing the symmetry of the complex bands and the decay rates for different wave vectors and energies we draw conclusions about spin-filter efficiency of EuO. Our results provide guidelines for the design of spin-filter tunnel junctions with enhanced spin polarization.


Comments
Copyright 2012 American Physical Society. Used by permission.