Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Alexei Gruverman Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
January 2005
Abstract
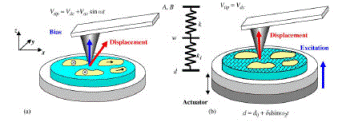
The ferroelectric domain structure and its dynamics under applied electric field have been studied with nanoscale resolution by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Two mechanisms responsible for the contrast between opposite domains are proposed: large built-in domains are delineated in friction mode due to the tip–sample electrostatic interaction, and small domains created by an external field are imaged in topography mode due to piezoelectric deformation of the crystal. The ability of effective control of ferroelectric domains by applying a voltage between the AFM tip and the bottom electrode is demonstrated. It is experimentally confirmed that the sidewise growth of domain proceeds through the nucleation process on the domain wall.


Comments
Published in J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 13(3), May/Jun 1995. Copyright ©1995 American Vacuum Society. Used by permission.