Biochemistry, Department of
Vadim Gladyshev Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
November 1999
Abstract
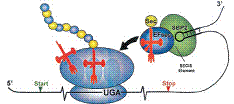
Mammalian selenium-containing proteins identified thus far contain selenium in the form of a selenocysteine residue encoded by UGA. These proteins lack common amino acid sequence motifs, but 3’-untranslated regions of selenoprotein genes contain a common stem-loop structure, selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) element, that is necessary for decoding UGA as selenocysteine rather than a stop signal. We describe here a computer program, SECISearch, that identifies mammalian selenoprotein genes by recognizing SECIS elements on the basis of their primary and secondary structures and free energy requirements. When SECISearch was applied to search human dbEST, two new mammalian selenoproteins, designated SelT and SelR, were identified. We determined their cDNA sequences and expressed them in a monkey cell line as fusion proteins with a green fluorescent protein. Incorporation of selenium into new proteins was confirmed by metabolic labeling with 75Se, and expression of SelT was additionally documented in immunoblot assays. SelT and SelR did not have homology to previously characterized proteins, but their putative homologs were detected in various organisms. SelR homologs were present in every organism characterized by complete genome sequencing. The data suggest applicability of SECISearch for identification of new selenoprotein genes in nucleotide data bases.


Comments
Published in Journal of Biological Chemistry 274:48 (November 26, 1999), pp. 33888–33897. http://www.jbc.org/. Copyright © 1999 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Used by permission.