Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Ilya Fabrikant Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2016
Citation
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 93, 032706 (2016)
Abstract
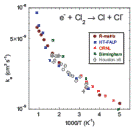
Thermal electron attachment rate coefficients for three interhalogen compounds (C1F, ICl, IBr) have been measured from 300 to 900 K at pressures of 1–2 Torr using a flowing afterglow–Langmuir probe apparatus. ClF attaches somewhat inefficiently (k = 7.5×10−9 cm3 s−1) at 300 K, with the rate coefficient rising to 1.7×10−8 cm3 s−1 at 700 K. At higher temperatures the apparent rate coefficient falls steeply; however, this is interpreted as an artifact due to decomposition on the walls of the inlet line. ICl attaches with even lower efficiency (k = 9.5×10−10 cm3 s−1 at 300 K) and a less steep increase with temperature. Attachment to IBr is too slow to confidently measure with the present experiment, with an upper limit on the rate coefficient of 10−10 cm3 s−1 from 300 to 600 K. Both ClF and ICl attach dissociatively to yield Cl−, likely exclusively, though F− or I− may be produced with limits of <2% and <5%, respectively. The ClF attachment was further explored through ab initio calculation of the ClF and ClF− potential energy curves and R-matrix calculations of the resonance parameters which were used then for calculations of the dissociative attachment cross sections and rate coefficients. While the magnitude of the attachment rate coefficient for ClF is similar to those for both Cl2 and F2, the calculated cross sections show qualitatively different threshold behavior due to the s-wave contribution allowed by the lack of inversion symmetry. The v = 1 and 2 vibrational modes of ClF attach about three to four times faster than v = 0 and 3 at energies lower than ∼0.2 eV. The calculated rate coefficients are in good agreement with the experiment at 300 K and increase moderately less steeply with temperature.


Comments
©2016 American Physical Society