Biochemistry, Department of
Vadim Gladyshev Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2008
Abstract
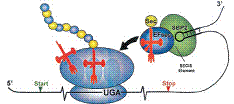
Synthesis of selenoproteins depends on decoding of the UGA stop codon as the amino acid selenocysteine (Sec). This process requires the presence of a Sec insertion sequence element (SECIS) in the 3’-untranslated region of selenoprotein mRNAs and its interaction with the SECIS binding protein 2 (SBP2). In humans, mutations in the SBP2-encoding gene Sec insertion sequence binding protein 2 (SECISBP2) that alter the amino acid sequence or cause splicing defects lead to abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Herein, we present the first in silico and in vivo functional characterization of alternative splicing of SECISBP2. We report a complex splicing pattern in the 5’-region of human SECISBP2, wherein at least eight splice variants encode five isoforms with varying N-terminal sequence. One of the isoforms, mtSBP2, contains a mitochondrial targeting sequence and localizes to mitochondria. Using a minigene-based in vivo splicing assay we characterized the splicing efficiency of several alternative transcripts, and show that the splicing event that creates mtSBP2 can be modulated by antisense oligonucleotides. Moreover, we show that full-length SBP2 and some alternatively spliced variants are subject to a coordinated transcriptional and translational regulation in response to ultraviolet type A irradiation-induced stress. Overall, our data broadens the functional scope of a housekeeping protein essential to selenium metabolism.


Comments
Published in Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, No. 22. Copyright © 2008 The Author(s). Used by permission.