Chemistry, Department of: Faculty Series
Patrick Dussault Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2013
Citation
J Org Chem. 2013 January 4; 78(1): 42–47.
Abstract
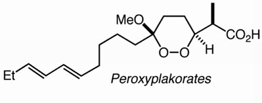
Several variants of reductive ozonolysis, defined here as the in situ generation of aldehydes or ketones during ozonolytic cleavage of alkenes, are demonstrated to work effectively in tandem with a number of C-C bond-forming reactions. For reactions involving basic nucleophiles (1,2- addition of Grignard reagents, Wittig or Horner-Emmons olefinations, and directed Aldol reactions of lithium enolates) the one-pot process offers a rapid and high-yielding alternative to traditional two-step protocols.
COinS


Comments
Copyright © 2012 American Chemical Society