Chemistry, Department of: Faculty Series
Robert Powers Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2006
Citation
J Am Chem Soc. 2006 November 29; 128(47): 15292–15299. doi:10.1021/ja0651759.
Abstract
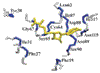
An abundance of protein structures emerging from structural genomics and the Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) are not amenable to ready functional assignment because of a lack of sequence and structural homology to proteins of known function. We describe a high-throughput NMR methodology (FAST-NMR) to annotate the biological function of novel proteins through the structural and sequence analysis of protein-ligand interactions. This is based on basic tenets of biochemistry where proteins with similar functions will have similar active sites and exhibit similar ligand binding interactions, despite global differences in sequence and structure. Protein-ligand interactions are determined through a tiered NMR screen using a library composed of compounds with known biological activity. A rapid co-structure is determined by combining the experimental identification of the ligand-binding site from NMR chemical shift perturbations with the proteinligand docking program AutoDock. Our CPASS (Comparison of Protein Active Site Structures) software and database is then used to compare this active site with proteins of known function. The methodology is demonstrated using unannotated protein SAV1430 from Staphylococcus aureus.


Comments
© 2006 American Chemical Society. Used by permission.