Center, Materials and Nanoscience, Nebraska Center for
Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience: Faculty Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2009
Abstract
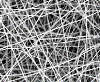
Alloys around the Sm–Co eutectic composition provide an opportunity to form two-phase nanocomposite permanent magnets consisting of nanoscale Co fibers embedded in Sm2Co17.While ternary alloying elements may refine the scale of the structure, they may also disrupt the eutectic growth and lead to the formation of primary Co. Thus, microstructural selection maps were constructed for conventionally solidified Sm–Co–V alloys. It was found that V additions enlarged the primary Sm2Co17-forming region and, at (Sm0.09Co0.91)97 V3, resulted in a eutectic structure. Upon rapid solidification, this alloy was determined to have a coercivity of 5 kOe with a high remanent ratio. However, the V addition reduced the magnetization, which limited the energy product to 4.3 MG Oe. The rapidly solidified structure consisted of primary SmCo7 dendrites along with an intergranular Co region, suggesting that eutectic structure formation is skewed by underlying metastable phase relationships.


Comments
Published in JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 105, 07A727 (2009). Copyright © 2009 American Institute of Physics. Used by permission.