Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Kirill Belashchenko Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2014
Citation
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 89, 174413 (2014)
Abstract
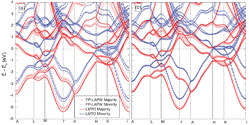
The exchange-driven contribution to the magnetoelectric susceptibility α is formulated using a microscopic model Hamiltonian coupling the spin degrees of freedom to lattice displacements and electric field, which may be constructed from first-principles data. Electronic and ionic contributions are sorted out, and the latter is resolved into a sum of contributions from different normal modes. If intrasublattice spin correlations can be neglected, the longitudinal component α becomes proportional to the product of magnetic susceptibility and sublattice magnetization in accordance with Rado’s phenomenological model. As an illustration, the method is applied to analyze the temperature dependence of the longitudinal magnetoelectric susceptibility of Cr2O3 using first-principles calculations and the quantum pair cluster approximation for magnetic thermodynamics. A substantial electronic contribution is found, which is opposite to the ionic part. The sensitivity of the results to the Hubbard U parameter and the sources of error are studied. It is also found that non-Heisenberg interactions are too weak to account for the sign change of α in Cr2O3.


Comments
©2014 American Physical Society