Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Peter Dowben Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
July 2006
Abstract
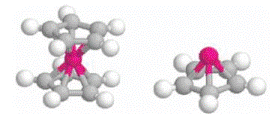
The bonding strength and interfacial electronic properties of biphenyldimethyldithiol (HS– CH2–C6H4–C6H4–CH2–SH) adsorbed on Au(111) and polycrystalline cobalt are identified from combined photoemission and inverse photoemission. In order to develop a better understanding of the thiol functional group to metal surface interaction, the stable orientation, bonding site, bonding strength and interfacial electronic properties of methylthiol (S–CH3) adsorbed on Au(111) and Co(0001) have been determined by ab initio density functional calculations. Both experiment and theory suggest that thiol bonding to cobalt surfaces is stronger compared to gold surfaces. The transfer of charge toward the adsorbed sulfur is greater for the thiols on cobalt than on gold.


Comments
Published in Journal of Materials Science. Published online July 6, 2006. Copyright © 2006 Springer Science + Business Media, LLC. Used by permission. DOI 10.1007/s10853-006-0362-7