Department of Physics and Astronomy: Individual Faculty Pages
Xia Hong Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2017
Citation
Applied Physics Letters (2017) 111: 182402
Abstract
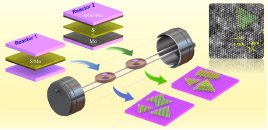
The interfacial charge transfer between mechanically exfoliated few-layer graphene and Cr2O3 (0001) surfaces has been investigated. Electrostatic force microscopy and Kelvin probe force microscopy studies point to hole doping of few-layer graphene, with up to a 150 meV shift in the Fermi level, an aspect that is confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. Density functional theory calculations furthermore confirm the p-type nature of the graphene/chromia interface and suggest that the chromia is able to induce a significant carrier spin polarization in the graphene layer. A large magnetoelectrically controlled magneto-resistance can therefore be anticipated in transistor structures based on this system, a finding important for developing graphene-based spintronic applications.


Comments
Used by permission