Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Robert Katz Publications
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
January 1995
Abstract
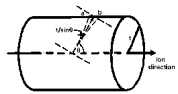
It has long been suggested that inactivation severely effects the probability of mutation by heavy ions in mammalian cells. Heavy ions have observed cross sections of inactivation that approach and sometimes exceed the geometric size of the cell nucleus in mammalian cells. In the track structure model of Katz the inactivation cross section is found by summing an inactivation probability over all impact parameters from the ion to the sensitive sites within the cell nucleus. The inactivation probability is evaluated using the dose-response of the system to γ-rays and the radial dose of the ions and may be equal to unity at small impact parameters for some ions. We show how the effects of inactivation may be taken into account in the evaluation of the mutation cross sections from heavy ions in the track structure model through correlation of sites for gene mutation and cell inactivation. The model is fit to available data for HPRT mutations in Chinese hamster cells and good agreement is found. The resulting calculations qualitatively show that mutation cross sections for heavy ions display minima at velocities where inactivation cross sections display maxima. Also, calculations show the high probability of mutation by relativistic heavy ions due to the radial extension of ions track from 6-rays in agreement with the microlesion concept. The effects of inactivation on mutations rates make it very unlikely that a single parameter such as LET or Z*2/β2 can be used to specify radiation quality for heavy ion bombardment.


Comments
Published in Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1995, Vol. 69, No. 5, 593-600.