Department of Physics and Astronomy: Publications and Other Research
Evgeny Tsymbal Publications
ORCID IDs
Tsymbal http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6728-5484
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
7-2006
Citation
Physical Review Letters (2006) 97: 047201
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.047201
Abstract
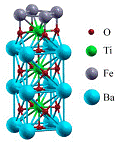
An unexplored physical mechanism which produces a magnetoelectric effect in ferroelectricferromagnetic multilayers is studied based on first-principles calculations. Its origin is a change in bonding at the ferroelectric-ferromagnet interface that alters the interface magnetization when the electric polarization reverses. Using Fe/BaTiO3 multilayers as a representative model, we show a sizable difference in magnetic moments of Fe and Ti atoms at the two interfaces dissimilar by the orientation of the local electric dipole moments. The predicted magnetoelectric effect opens a new direction to control magnetic properties of thin-film layered structures by electric fields.


Comments
Copyright © 2006, American Physical Society. Used by permission