Papers in the Biological Sciences
Document Type
Article
Date of this Version
2004
Citation
Published in Journal of Microbiological Methods 56 (2004) 119– 124.
DOI: doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2003.09.021
Abstract
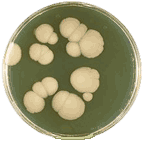
A method is described for the formation of nearly 100% pseudohyphae populations of wild-type Candida albicans A72. The method employs fungal growth at 37 °C (ca. 5×106 cells/ml) in a glucose–proline–N-acetyl-glucosamine medium supplemented with up to 600 mM phosphate (KH2PO4/K2HPO4 1:1) at pH 6.5. Four other strains of C. albicans (MEN, 10261, SG5314 and CAI-4) also formed pseudohyphae under these conditions, although the phosphate response profiles differed in the concentration required for each strain to form pseudohyphae.
Included in
Environmental Microbiology and Microbial Ecology Commons, Other Life Sciences Commons, Pathogenic Microbiology Commons


Comments
Copyright © 2003 Elsevier B.V. Used by permission.